Visualizing Data with GIS
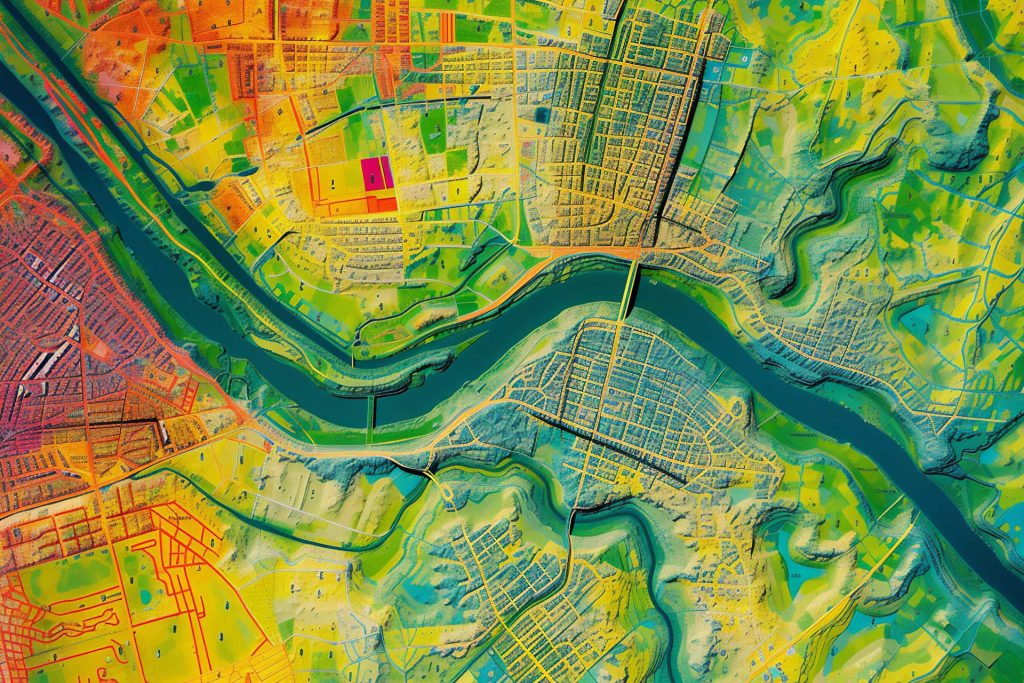


Unlocking Geographical Data Insights (GIS)
GIS Enhances Organizational Efficiency
GIS has a wide range of economic and strategy benefits to various types and sizes of organizations and industries. There is a growing awareness of usage of GID in part because of data standardizing and in part because of quantum leaps in the computing power and applications necessary to capture and analyze this data.
GIS applications aim to increase efficiency, improve communication and decision making, and allow geographical management, tracking, and recordkeeping. Examples range from Google Maps and transportation fleet optimization, to disaster response and augmented reality games and applications like Pokemon Go. Academic and political institutions have begun looking to GIS for insight into public health, environmental concerns, archeology and demographics.
Comprehensive GIS Data Solutions
GIS Implementation
Takes the design and creates a system and operational reality from the requirements and design phase through the built-out phase, to the implementation phase. GIS implementation takes the design and creates a system and operational reality from the requirements and design phase through the built-out phase, to the implementation phase. Best practices GIS implementations should include initial testing of the systems and operations, installation, final delivery, user training, operational migration, and then ongoing GIS maintenance.
Data Format Conversion
Is often a key component in making sure that the data can be used. Data format conversion is often a key component in making sure that the data can be used. An example is the conversion of an aerial or satellite image map to a vector structure. This groups cells of similar data together while determining spatial relationships like inclusion and adjacency.
GIS Needs Assessment
Is often a key component in making sure that the data can be used. GIS needs assessment is the first step in determining the usefulness and viability of GIS data and systems to an organization. During the needs assessment part of the process, staff and stakeholder interviews are conducted and an inventory of existing hardcopy and electronic geographical data is taken. Potential efficiencies and areas of cost savings are analyzed and presented in order to generate a list of GIS related priorities.

Special Problem Analysis
With more people and systems than ever before accessing the power of GIS technology and spatial information, various problems can manifest in the GIS data, which can compromise the quality of existing data. Special problem analysis with more people and systems than ever before accessing the power of GIS technology and spatial information, various problems can manifest in the GIS data, which can compromise the quality of existing data. Drivers of this compromise can include the high volume of systems accessing GIS data, the rapid advance of technology populating GIS data, and the elementary forms of GIS information that can conflict with professional registered surveyor mapping points.
GIS Maintenance
This includes the ability to maintenance existing hard-copy data as well as those in digital formats. GIS maintenance this includes the ability to maintenance existing hard-copy data as well as those in digital formats. Either confirming or updating existing points due to topographic change is crucial for accurate surveying, platting, and mapping functions. This maintenance can include using various systems, including MicroStation and CAD, to reproduce visual representation of the GIS points.
GIS Design and Development
Uses the output from the GIS needs assessment process to create a system architecture plan. GIS design and development uses the output from the GIS needs assessment process to create a system architecture plan. Proper design includes the relationships between business needs, data availability, format, and storage, and the analytical and computational technology.


